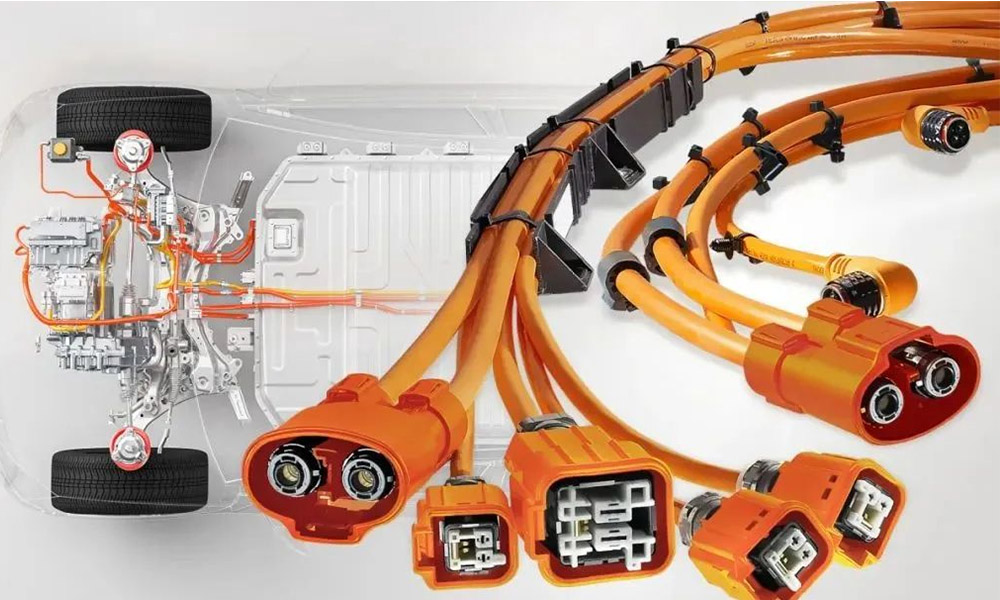
The Art of Signal Synchronization: Unveiling the Technological Mysteries of Matching Cable Assemblies
In modern electronic systems, signal transmission is like a precise symphony performance. And the matching cable assembly is the indispensable conductor in this performance, ensuring that each electronic signal can be perfectly synchronized and resonate harmoniously.
I. What is a matching cable assembly?
Imagine that in a light show at a large stadium, thousands of LED lights need to flash completely synchronously to present a perfect visual effect. The role of matching cable assemblies in electronic systems is similar - they are specially designed and precisely manufactured RF cables that can ensure that multiple signals maintain strict time synchronization during transmission.
The core technology of these cables lies in "electrical length matching", that is, maintaining a consistent signal transmission time at a specific operating frequency (usually expressed in phase angles). In 5G communication base stations, this synchronization accuracy can reach an astonishing phase difference of less than 1 degree, equivalent to a time synchronization accuracy of several picoseconds (1 picosecond = one trillionth of a second).
II. Why are these components so crucial?
In today's rapidly developing electronic world, matching cable assemblies have become indispensable basic components in many high-tech fields:
Phased array radar system: The phased array radar on modern warships may contain thousands of radiation units, and the signals of each unit must be strictly synchronized. If there is an error in synchronization, it may lead to a deviation in target positioning. After the error is magnified, the difference may be several kilometers.
2. 5G/6G communication networks: Large-scale MIMO antenna systems need to handle hundreds of data streams simultaneously. In the millimeter-wave frequency band, even a difference of a few millimeters in cable length can cause the signal to completely lose synchronization.
3. Satellite communication system: In the geosynchronous orbit at an altitude of 36,000 kilometers, satellites need to maintain precise phase relationships with ground stations. Any signal desynchronization may lead to communication interruption.
4. Medical imaging equipment: MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) machines need to precisely control the phase of radiofrequency signals to reconstruct clear images of human tissues. Phase error can cause artifacts in the image, affecting the accuracy of diagnosis.
III. Manufacturing Process: An art of precision to the extreme
Manufacturing high-quality matching cable assemblies can be regarded as a model of modern precision manufacturing. The entire process requires breaking through multiple technical limits:
Breakthroughs in materials science
Conductor material: Ultra-high purity oxygen-free copper (with a purity of over 99.99%) is used, and the surface is silver-plated to reduce high-frequency loss
Insulating material: Expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is adopted, with a dielectric constant stabilized at 2.1±0.05
Shielding layer: Multi-layer silver-plated copper tape braided, with a shielding efficiency of over 90dB
2. Precision manufacturing process
Length control: Measured by a laser interferometer with an accuracy of ±0.01mm/m
Termination process: The connector is processed by a high-precision CNC machine tool, with a concentricity deviation of less than 0.02mm
Phase matching: Minor differences are compensated through electronic tuning technology, with a matching accuracy of ±0.5°
3. Rigorous testing and verification
Phase stability test: The phase change is less than 2° within the temperature range of -55℃ to +125℃
Mechanical durability test: The performance change does not exceed 1% after 500 insertions and removals
Environmental testing: including multiple rigorous tests such as vibration, shock, and salt spray
IV. Analysis of Typical Application Scenarios
Phased array radar system
In the Patriot air Defense missile system, its AN/MPQ-53 radar contains more than 5,000 radiation units. Each unit requires strict phase control in order to achieve precise beam pointing. The matching cables here ensure that the excitation signals of each unit maintain an accurate phase relationship, enabling the radar to track hundreds of targets simultaneously.
2. 5G Massive MIMO
In the 192-antenna array of 5G base stations, each antenna requires an independent radio frequency channel. After using the matching cable assembly, the system can achieve a phase consistency of ±1°, increasing the spectral efficiency by more than three times.
3. Quantum communication system
In quantum key distribution systems, signals at the single-photon level need to maintain precise phase relationships. The specially designed matching cable can control the signal loss within 0.1dB/m while maintaining phase stability.
V. Future Development Trends
With technological advancements, matching cable assemblies are developing rapidly in three directions:
Higher frequency: Supports the 110GHz TeraHertz frequency band, with phase stability better than ±0.5°
2. Smaller size: Develop miniaturized solutions, with ultra-fine matching cables with a diameter of less than 1mm
3. More intelligent: Integrating temperature sensors and compensation algorithms to achieve real-time phase calibration
It is particularly worth mentioning that in the upcoming 6G era, terahertz communication poses more stringent requirements for the corresponding cables. Researchers are developing new cable structures based on novel metamaterials, which are expected to achieve breakthrough performance in the 300GHz frequency band.
Conclusion
From deep-sea probes to deep-space telescopes, from smart phones to smart healthcare, the matching cable assemblies silently support every significant breakthrough in modern technology. They may be hidden inside the devices and not seen by others, but it is precisely these precise components that ensure our digital world can operate precisely and reliably.
With the development of new technologies such as the Internet of Things and artificial intelligence, the requirements for signal synchronization accuracy will only become higher and higher. The technological innovation of matching cable assemblies will continue to drive the pace of human technological progress.